Page 138 - Prathima Volume 12
P. 138
The impact of Influencer Culture on Digital Hyper-Reality:
A Case Study on the Food Consumption Patterns of Sri Lankan Urban Youth
However, a 72% (38) majority of responded that they do not tend to follow the reviews
of the social media influencers due to reasons such as taste being a highly subjective
concept, influencers been sponsored to promote brands which create biases, issue of
ignoring vegetarian food being reviewed, and them considering that what is depicted
in social media can be different in reality. The above findings could be argued in line
with the concept of hyper-reality in the context of social media as explained by Jean
Baudrillard (1976). Due to the said reasons 50% (27) of the sample was neutral in
agreeing with the (food) reviews of the food reviewers. However, 39% (19) did
mention that they agree with the reviews of the influencers more often. It was notable
that a majority of 45% (23) have sometimes regretted in taking up food choices based
on the influencer reviews. However, 33% (17) have responded that they have never
regretted such decisions due to the reasons of such reviews been accurate and well
detailed.
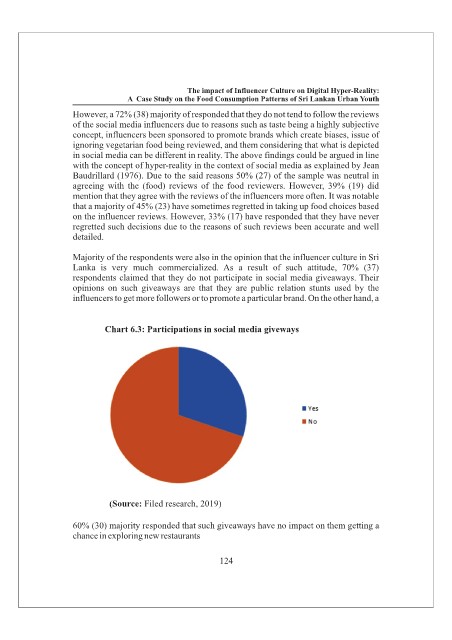
Majority of the respondents were also in the opinion that the influencer culture in Sri
Lanka is very much commercialized. As a result of such attitude, 70% (37)
respondents claimed that they do not participate in social media giveaways. Their
opinions on such giveaways are that they are public relation stunts used by the
influencers to get more followers or to promote a particular brand. On the other hand, a
Chart 6.3: Participations in social media giveways
(Source: Filed research, 2019)
60% (30) majority responded that such giveaways have no impact on them getting a
chance in exploring new restaurants
124